 |
| Teeth Scaling on Myself by The Dentist in Dakota Branch SB Dental, Bandung, Indonesia |
All About Health💪 & Humanity👥
Reasonable Empathy: Good for Our Mental Healthcare. Thx for Visiting My Blog, may Allah Bless All of Us. Aamiin
Sunday, June 1, 2025
The Importance of Teeth Scaling to Prevent more Serious Diseases
Tuesday, December 3, 2024
Tips for Maintaining Mental Health in The Digital Era
World Mental Health Day is celebrated every year on October 10, exactly a month ago. This warning aims to increase public awareness and concern for the importance of mental health. Now we live in the digital era, where mental health problems are not only related to the real world, but also the virtual world. Everything must receive equal attention. However, for this article, I am only focusing on mental health in cyberspace.
Often we see information on social media or internet that is not balanced between positive and negative things. Of course, it would be useful to get positive information about new knowledge, new experiences, productive activities, something creative, and entertaining. On the other hand, your mind will get anxious, bored, stressed, wasting time, and gives rise to jealously if you see negative information, such as hoax, criminal news, hate speech, and flexing content. Therefore, for this reason, we must be wise in using social media. If you feel it is not useful, it is better to stop first.
Here tips for maintaing mental health in the digital era:
1. Strive for quality sleep. The ideal sleep for an adult is 5-8 hours a day. Don't be less or more. Before going to bed, make sure the lights are dim, the bed is comfortable, the air circulation is good & smells good, no mosquitos, gadgets are turned off, & you can set the alarm. Quality sleep is important, so that the body is healthy, fit, relax, & happy to welcome the next day. A good mood means good mental health
2. Impose time restrictions, if necessary a day without social media excepts for work needs, learn new knowledge, important means of communication, & looking for more luck. Don't let our minds be filled with toxic content. This is often called social media detox
3. Limit interactions, respect the privacy of yourself & the others on social media. However, positive interactions in the real world are more important
4. Reduce curiocity about people's lives because it can make us stressed & less grateful. It's better to find out our weaknesses and immedeately improve yourself
5. Adopt healthy lifestyle and be disciplined in prioriting activities. Play social media & internet only for things that are useful. Even if you are tired, you have to rest because you also have to maintain eye health
6. If you bored due to using gadget, try healing either alone, with family, or friends with the same hobby
Please also come to my first blog (about innovation, law, management, & soccer, full text Indonesia), third blog (about problems & electrical solutions, full text Indonesia), and fourth blog (about pets, full text Indonesia). May be useful. Thx. Here's the link:
Blog 1: vickycahyagi.com
Blog 3: listrikvic.blogspot.com
Blog 4: petsvic.blogspot.com
Thursday, February 1, 2024
Sport must Involve Strong Physical Movement, How about Chess?
How about chess, one of individual sports? Altough chess was official sport, I often hear people say that chess was inappropriate called sport until now because it didn't involve strong physical movement. It only about think and think activity. Move the chest piece was not strong physical movement. Chess didn't take a lot of sweat. But, there was opinion against it. Think activity is part of brain sport. Practice brain skill for many hours in one professional chess match needs physical strength. I see that one professional chess match spend 6 hours. Chess learn about individual strategy to win the game with many plans. In my opinion, in chess match, if we have a bad physique, mood, patience, and mental, we will lose the game easily. So, before the match, we must keep our fitness. All of it was become element of sport. I agree and pro about chess was a sport, but I respect the people who disagree with that.
 |
| Source: azquotes.com |
When we play chess under pressure (not for entertainment, not for fun, but for carry the name of the country), so we will spend take a lot of sweat, because we are in tense condition. It remove a lot of fluids. The activity that remove a lot of fluids could be called sport. So, we have to look view of the whole part, not a half part, and sure that chess deserves to be called sport. Besude that, we must plan the certain exercise, not only physics, but also mental, before the match.
Please also come to my first blog (about innovation, law, management, & soccer, full text Indonesia), third blog (about problems & electrical solutions, full text Indonesia), and fourth blog (about pets, full text Indonesia). May be useful. Thx. Here's the link:
Thursday, February 2, 2023
Basic Physical Non-Trauma Life Support
3. Sink down
Source: aladokter.com,& halodoc.com, hellosehat.com.
 |
| Workhop about Basic Life Support (Non-trauma) from Bandung Fakerunners Community Cooperates with SIAGA & AGD 118. Source: Pikiran Rakyat Newspaper |
Sunday, January 1, 2023
Basic Trauma Life Support
- Compress the lump with ice for 15 minutes and repeat every hour
- After the bumps are reduced, but there are still bruisses, compress with warm water
- Gentle massage the bruish with the thumb. Massage in a circular motion
- Drying bruises for about 10 minutes
- If there is bleeding, stop bleeding with a clean cloth or sterile gauze, clean the wound+dirt on the wound with running water, give antiseptic and cover with plester
- If the victim has a broken bone and shifted,
 |
| Source: vice.com & aladokter.com |
c. Got electric shock
Monday, August 8, 2022
International Cat Day: Having a Cat for Health and Mental Wellbeing
Today, August 8, we are celebrating International (World) Cat Day, so we have to respect their existence as an ecosystem that is beneficial to humans to. I want share the information that having a cat is good for health and mental wellbeing:
1. Reduce stress and anxiety
- Can cause the body to produce relaxing hormones, such as endorphins, that help lower your tension and anxiety levels
- Cultivate a positive mood
2. They can lower the risk of hearth disease and stroke
- According to study published in the Journal of Vascular and Interventional Neurology, having a cat can reduce stress, thus reducing the risk of developing various hearth illness, including stroke, by roughly 30 %
- Of course, it's good to increase the body's immunity
3. They help prevent allergies (for children)
- The National Institutes of Health published a study in 2002 that indicated hildren under a year old who were esposed to a cat were less likely to have allergies of any sort, such as dust mites, ragweed, and grass
- Of course, cat hygiene must be maintained
4. Prevent loneliness and fear
- Cat behavior can make people forget they are alone at home
- Cats are believed to be animals that devils doesn't like
- Cats are animals that snakes hate, especially small snakes
5. Having a cat can foster social sensitivity
- We will appreciate the environment more
- We will increasingly realize that life interdependent in an ecosystem
- Practice caring for fellow human beings
6. As a part of charity good deeds
- Because cats is a creature created by God that must be taken care with the help of humans
- Good deeds return to us in uxpected conditions
- As a part of gratitude to God.
I have two male cats pets, named Cowy and Bar-Bar. They are the type of domestic cat that rarely gets sick and is easy to manage. They are always bathed once a week.
Ok, if you want to share other information about cat, please share in the comment column🙏🏻. Happy International Cat Day🐱.
Please also come to my first blog (about animals, innovation, law, management, & soccer, full text Indonesia), third blog (about problems & electrical solutions, full text Indonesia), and fourth blog (about pets, full text Indonesia). May be useful. Thx. Here's the link:
Blog 1: vickycahyagi.com
Blog 3: listrikvic.blogspot.com
Blog 4: petsvic.blogspot.com
Tuesday, March 8, 2022
Have you been Vaccinated with The COVID-19 Booster?
Hello blogger friends from all over the world, how are you? I hope that you will continue to be given blessings, health, and the spirit of writing. Aamiin😇. This is the first article on my second blog (english blog) in 2022. Hopefully, this article about COVID-19 will be last, in the sense that the COVID-19 pandemic ends this year😊.
In my country, Indonesia, the permitted COVID-19 booster vaccine include AstraZeneca, Moderna, Pfizer, Sinopharm, Sinovac, Zivivax. But the one with the most stock is AstraZeneca. Even though is much cheaper than other COVID-19 vaccines, because the inventor didn't patent AstraZeneca, puts the human side forward, but don't neglect quality.
Surprisingly, many looking for Pfizer because it is considered more effective, suitable for commorbidities, and has a few side effects. But, as far as I can see, someone got the COVID-19 booster Pfizer vaccine, then a few days had a fever. While my father who is 70 years old, has comorbidities, and gets the COVID-19 booster AstraZeneca vaccine, it did not serious side effects. Just sleepy and easily hungry. So, everything is returned to the immune and body condition of each individual. If you are worried that you have side effects and attack comorbidities, you should first consult with your doctor. Each COVID-19 vaccine, include booster, that have been recognized by the government, has its own advantages and disadvantages.
I got the COVID-19 booster vaccine (the third vaccine) on February 17, 2022. after 6 months (the latest rules are enough 3 months apart) of the second dose of COVID-19 vaccine on August 12, 2021. For the first and second COVID-19 vaccines using Sinovac, while boosters use AstraZeneca. I didn't get any serious side effects when vaccinated sinovac. However, I got side effects from AstraZeneca booster vaccine in the form of joint pain in my right legs for 2 days. I got my all my vaccine at a community health center near my house, with a limited quota and 2 times a week. When I recovered, I became more confident to go outside, of course, by continuing by carry out health protocols.
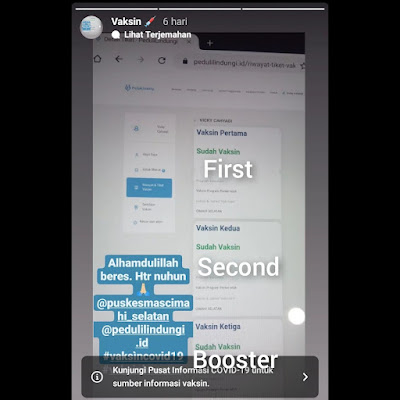 |
| In Indonesia, Data for Every Citizen who has been Vaccinated and Other Information Related to Vaccines and COVID-19 is Integrated in One Application: Pedulilindungi.id |
Now, the Indonesian government has a made a new rule that when travelling using public transportation such as trains and planes, it is not necessary to have an antigen/PCR test provided that you have been fully vaccinated, at least the second vaccine. This is of course good news, although there are still concern that people will not obey health protocols, especially during long holidays. There is even a new rule for the Eid holiday after Ramadan, everyone who returns to their hometown must have a The COVID-19 booster vaccination. Of course, there are exceptions, for those who are prohibited from vaccines by including a doctor's letter. zIf it's just the second vaccine, it still has to be tested for Antigen or PCR.
There is a plan from the government about the 4th COVID-19 vaccine or the second booster vaccine. I think as long as it has been scientifically tested and proven have a new variant, of course it should be supported. Hopefully there won't be a new variant and the first booster vaccine will suffice.
Lastly, I also want to know your condition after being vaccinated. Have you been vaccinated with the COVID-19 booster? what type of vaccine? Are there any side effects? or something else about COVID-19 vaccines? Please share in the comments column. Thanks. Stay safe and healthy.
Please also come to my first blog (about animals, innovation, law, management, & soccer, full text Indonesia), third blog (about problems & electrical solutions, full text Indonesia), and fourth blog (about pets, full text Indonesia). May be useful. Thx. Here's the link:
Blog 1: vickycahyagi.com
Blog 3: listrikvic.blogspot.com
Blog 4: petsvic.blogspot.com
Monday, October 4, 2021
List of COVID-19 Vaccines Recognized by WHO
COVID-19 vaccines recognized by WHO (World Health Organization) and given permission Emergency Use Listing (EUL) if it meets the requirements:
1. Quality
Related to the characteristics of the vaccine:
- Vaccine type
- Vaccine composition
- How to inject
2. Safety
- Reasonable side effect
- Safe for eligible ederly
- Safe for eligible children 12 years and over
3. Vaccine efficacy level
- Efficacy is how well a vaccine works in clinical trials
- Must be above 50 %
4. Effectiveness level
- Effectiveness is how well a vaccine is given to the general public
- Must be above 50 %
5. Vaccine manufacturing
Directed to become an industry
6. Risk management plan
- Careful and precide screening process for vaccine recipients
- Solution in case of unnatural vaccine side effects.
The assessment is carried out by experts from all over the world and Technical Advisory Group, to provide assessment of benefits, risks, and recommendations.
List of Covid-19 Vaccines recognized by WHO:
1. Pfizer-BioNTech
- The first vaccine recognized by WHO and get EUL on December 31, 2020
- Made in the United States
- Double dose (interval 3 weeks)
- Vaccine type: nucleic acid vaccine
- Strength: has a strong cellular immunity and fast development
- Weaknesss:
a. Relatively low antibody response. As a result, the body's response to infection works more slowly
b. Must be stored in a frozen state
2. AstraZenenca
- Recognized by WHO anda get EUL on February 15, 2021
- Made in South Korea and India
- Double dose (interval 2-3 months)
- Vaccine type: viral-vector virus, replicating or non-replicating
- Viral-vector is a harmless virus modified to trigger an immune response
- Strength:
a. Fast development
b. Cheap price (not subjects to patents and assisted by the role of non-profits organizations)
c. Can be stored at normal refrigerator temperatures
- Weakness:
a. Previous exposure to viral vectors may reduce immunogenicity
Immunogenicity is the ability of a substance to trigger an immune response from the human body or other animals
3. Johnson & Johnson
- Recognized by WHO and get EUL on March 12, 2021
- Made in the United States
- Only single dose
- Vaccine type: adenovirus type 26, which inserts corona virus proteins into body cells and triggers an immune response
- Strength:
a. Only single dose. Of course it really helps to reach difficult areas
b. Can be stored at normal refrigerator temperatures
- Weakness: potentially cause an allergic reaction
4. Moderna
- Recognized by WHO and get EUL on April 30, 2021
- Made in the United States
- Double dose (interval 1 month)
- Vaccine type: nucleic acid vaccine
- Strength: has a strong cellular immunity and fast development
- Weaknesss:
a. Relatively low antibody response. As a result, the body's response to infection works more slowly
b. Must be stored in a frozen state
5. Sinopharm
- Recognized by WHO and get EUL on May 7, 2021
- Made in China
- Double dose (interval 3 weeks)
- Vaccine type: inactivated vaccine
- Strength:
a. Induce a strong immune response
b. Can be stored at normal refrigerator temperatures
- Weakness: when the manufacturing process, requires a lot of viruses.
6. Sinovac
- Recognized by WHO and get EUL on January 6, 2021
- Made in China
- Double dose (interval 1 month)
- Vaccine type: inactivated vaccine
- Strength:
a. Induce a strong immune response
b. Can be stored at normal refrigerator temperatures
- Weakness: when the manufacturing process, requires a lot of viruses
(source: klinikpintar.id & news.detik.com).
COVID-19 vaccines that are applicable in my country, Indonesia, include: Sinovac, AstraZeneca, Sinopharm, Moderna, and Pfizer-BioNTech. However, Sinovac vaccine is most used. I also was injected by the Sinovac Vaccine (double dose). The effect that I feel (one day after injection) is only soreness in the area of the injection site, hunger pang, and drowsiness. After that, it's back to normal. How about you? Please comments in the comments column. Thank you, stay safe and healthy. God blessed us🙏.
 |
| Source: Ciputrahospital.com |


